Wound Care & Skin Grafting
Warning: The images of this page are graphic in nature. Below are actual foot wounds
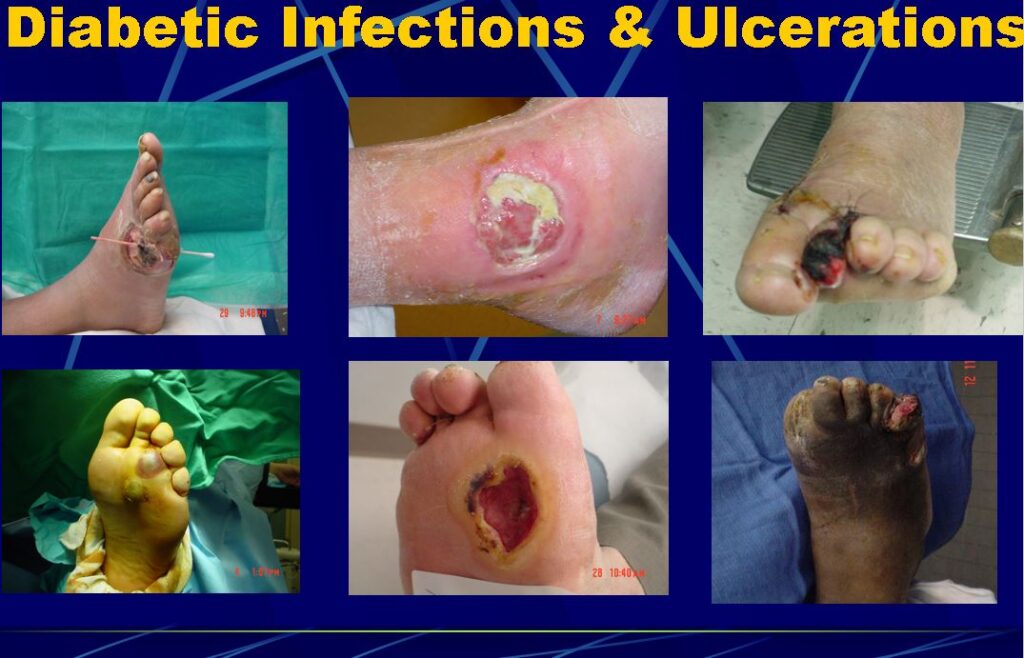
Treatment of Diabetic Foot Wounds: A Comprehensive Approach to Amputation Prevention
2 Things that need to occur with any foot wound:
1. Getting healed
2. Staying healed!
Managing diabetic foot wounds requires a multidisciplinary approach to effectively promote healing and prevent complications such as amputation. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot ulcers due to poor circulation, nerve damage, and impaired immune function. To ensure optimal outcomes, a comprehensive treatment plan should be implemented.
Major Causes of Diabetic Foot Wounds
- Poor glycemic control
- Duration of diabetes
- Improper foot care
- Ill-fitting footwear
- Underlying peripheral neuropathy
- Poor circulation
- Dry skin
- Calluses
- Foot deformities
Experiencing Foot or Ankle Pain?
We’re here to help! Contact our friendly staff and connect with our expert doctors
Diabetic Foot Wounds Treatment
Here’s an overview of the key components involved in the treatment of diabetic foot wounds with a focus on amputation prevention.
- Wound Assessment and Classification: The first step in the treatment process is a thorough assessment of the wound. This includes evaluating its size, depth, location, and the presence of infection. A classification system, such as the Wagner or the University of Texas Wound Classification System, helps determine the severity of the wound and guides treatment decisions
- Offloading Pressure: Reducing pressure on the wound is crucial for successful healing. Offloading techniques, such as the use of specialized footwear, custom orthotics, or removable casts, help redistribute pressure away from the affected area. This can be supplemented by patient education on proper foot care and footwear selection to prevent recurrent pressure points.
- Wound Debridement: Removal of dead or infected tissue through debridement is essential to create an optimal environment for healing. Debridement can be performed through various methods, including sharp debridement, enzymatic agents, or advanced wound dressings. Regular debridement sessions may be necessary until the wound shows signs of healthy tissue.
- Infection Management: Diabetic foot wounds are susceptible to infection, which can significantly impede the healing process. Prompt identification and management of infections are crucial. This typically involves taking wound cultures, prescribing appropriate antibiotics if necessary, and closely monitoring the wound for signs of infection resolution.
- Advanced Wound Dressings: Applying appropriate wound dressings is vital for maintaining a moist wound environment and promoting healing. Advanced wound dressings, such as hydrogels, foams, or films, can help manage exudate, protect the wound from external contaminants, and facilitate tissue regeneration. The choice of dressing depends on the characteristics of the wound and the stage of healing.
- Vascular Assessment and Revascularization: Poor blood circulation is a common complication in diabetes, impairing wound healing. Therefore, a vascular assessment is essential to evaluate the blood flow to the lower extremities. If significant vascular disease is present, revascularization procedures, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, may be considered to improve blood supply and enhance healing potential.
- Blood Glucose Control: Achieving and maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is paramount in diabetic wound healing. Elevated blood sugar levels hinder the body’s natural healing processes. Close collaboration with endocrinologists or primary care physicians is necessary to manage diabetes effectively and achieve target glucose control.
- Patient Education and Self-care: Empowering patients with knowledge about foot care and wound management is essential for long-term success. Patients should receive education on proper foot hygiene, daily foot inspections, and prevention strategies to minimize the risk of future wounds. Self-care techniques, such as regular moisturization and nail trimming, should be discussed with their doctor before anything is attempted.
- Rehabilitation and Monitoring: Rehabilitation plays a vital role in restoring functionality and preventing recurrence. Physical therapy may be recommended to improve gait mechanics, strength, and flexibility. Regular follow-up visits with a healthcare team, including podiatrists, wound care podiatrist, and diabetes educators, are crucial to monitor wound progress, adjust treatment plans, and ensure ongoing preventive measures.
By adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses all aspects of diabetic foot wound management, including wound assessment, offloading pressure, infection management, advanced wound dressings, vascular assessment, blood glucose control, patient education, and rehabilitation
In the vast majority of cases (98%), the condition is successfully treated with conservative measures. In the minority of cases that do not respond completely with conservative measures, there are modern minimally-invasive surgical procedures to address the condition
Wound Care Modalities Used at We Treat Feet Podiatry
Wound care modalities refer to various methods and techniques used to treat and manage wounds. At WeTreatFeet Podiatry, we specialize in advanced wound care treatment. The risk of amputation and death is very elevated with diabetes. Over the counter wound medications are seldom sufficient for wound care. Please read the labels of all of these medications before applying them to your foot. Call us if you want a consultation for the most advanced wound care available.
Cleaning and irrigation
This involves washing the wound with a mild cleanser or sterile saline solution to remove debris and bacteria.
Dressings
Different types of dressings, such as adhesive, gauze, hydrocolloid, or foam dressings, can be used to protect the wound, promote healing, and maintain a moist environment.
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT)
This involves the application of a vacuum dressing to the wound, which helps to promote healing and remove excess fluid.
Debridement
This process involves the removal of dead or damaged tissue from the wound to facilitate healing. It can be done through surgical, mechanical, enzymatic, or autolytic methods.
Compression therapy
Compression bandages or garments are used to apply pressure on the wound and surrounding tissues to reduce swelling, promote circulation, and aid in healing.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT):
In HBOT, the patient is exposed to 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which helps to increase oxygen levels in the blood and enhance wound healing.
Topical medications
Various topical ointments, creams, or gels may be used to prevent infection, promote healing, or manage specific wound conditions, such as antimicrobial agents or growth factors.
Biological dressings
These include the use of biological materials, such as skin grafts or synthetic substitutes, to cover the wound and promote healing.
Electrical stimulation
Electrical currents can be applied to the wound to stimulate tissue growth and enhance healing.
Laser therapy
Low-level laser therapy can be used to promote wound healing by stimulating cell activity and increasing blood flow.
Surgical interventions
In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair and close complex or severe wounds.
Patient education and support
Proper wound care techniques, hygiene practices, and lifestyle modifications are essential, along with emotional support and counseling to promote patient well-being during the healing process.
Experiencing Foot or Ankle Pain?
We’re here to help! Contact our friendly staff and connect with our expert doctors
