Understanding Bunions
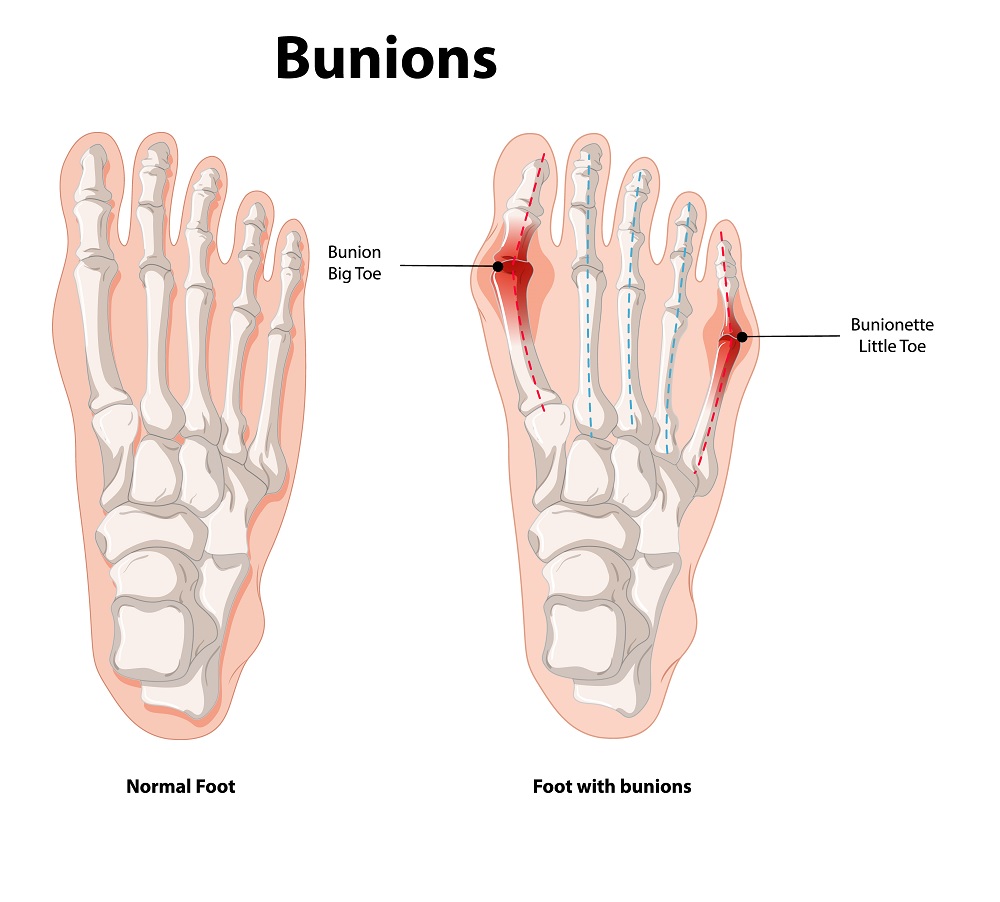
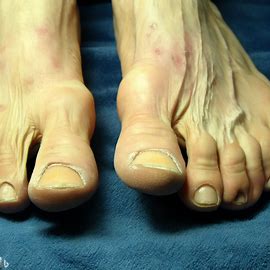
Bunions, medically known as hallux valgus, are bony bumps that develop on the joint at the base of the big toe. This condition occurs when the big toe pushes against the adjacent toe, causing the joint to protrude and become misaligned. Bunions can be painful and may gradually worsen over time if left untreated.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of bunions, including:
- Genetics: A family history of bunions increases the likelihood of developing this condition.
- Foot Structure: Certain foot types, such as flat feet or low arches, can make individuals more prone to developing bunions.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing tight, narrow, or high-heeled shoes can squeeze the toes together and increase the risk of bunions.
- Joint Conditions: Some underlying joint conditions, such as arthritis, can contribute to the development of bunions.
- Gender: Bunions are more common in women, possibly due to the frequent use of tight-fitting shoes.
Symptoms and Complications
Bunions can cause a range of symptoms and complications, including:
- Bulging Bump: A visible bump on the base of the big toe is a common sign of a bunion.
- Toe Misalignment: The big toe may lean toward the adjacent toe, causing it to overlap or push against the other toes.
- Pain and Discomfort: Bunions can be painful, especially when walking or wearing tight shoes.
- Restricted Movement: The misalignment of the toe joint can restrict its range of motion and affect foot function.
- Calluses and Corns: The friction caused by bunions can lead to the development of calluses and corns on the affected area.
Effective Treatment Options
- Comfortable Footwear: Wearing properly fitted shoes with a wide toe box can help alleviate bunion-related pain and discomfort. Choose shoes that provide ample space for your toes to move freely.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom-made shoe inserts or orthotic devices can provide support, improve foot alignment, and relieve pressure on the bunion.
- Padding and Taping: Applying protective padding or using special bunion tapes can help reduce friction and alleviate pain.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation associated with bunions.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises and stretches prescribed by a physical therapist can strengthen the foot muscles, improve flexibility, and promote proper alignment.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, bunion surgery may be considered. Surgery aims to realign the toe joint and remove the bony protrusion.
Prevention Tips
To prevent bunions or slow down their progression:
- Choose Appropriate Footwear: Opt for comfortable shoes with a wide toe box and low heels.
- Avoid Tight Shoes: Avoid footwear that squeezes or cramps your toes together.
- Maintain Healthy Foot Mechanics: Practice exercises that strengthen the foot muscles and promote proper alignment.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have arthritis or other joint conditions, work with your healthcare provider to manage them effectively.
Conclusion
Bunions can cause discomfort and affect foot health, but with the right knowledge and interventions, you can find relief and improve your condition. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring the effective treatment options, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy and pain-free feet. Don’t let bunions hinder your mobility and well-being—seek appropriate care and embrace preventive measures for optimal foot health. Click here to make an appointment with a WeTreatFeet Podiatrist